Focal length is often a photographer’s first consideration when deciding what lens to use to capture a given scene or subject. But what is focal length? And how do photographers use it to create compelling images?
Focal Length Definition
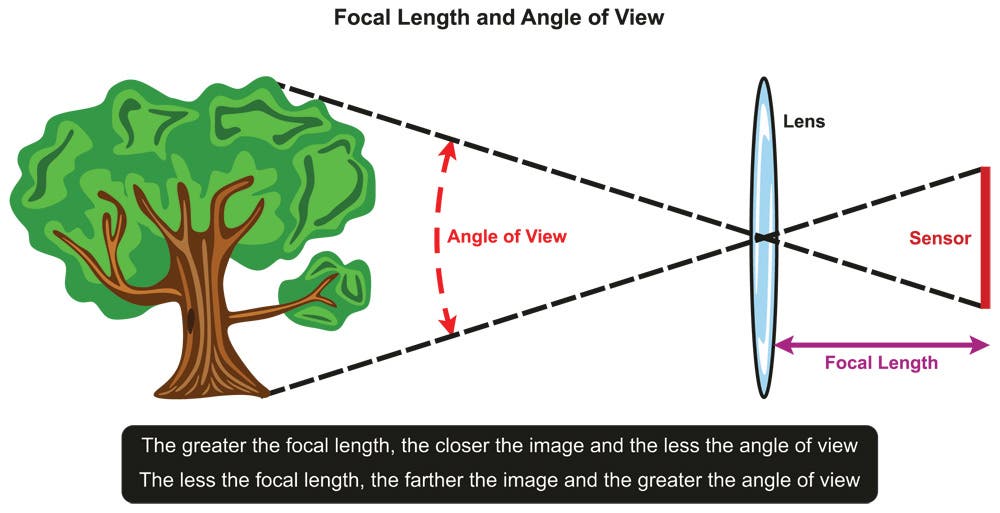
Focal length is the distance measured in millimeters, between the optical center of the lens and the camera sensor, where the light information is recorded. When light enters the front of a lens, the elements inside the housing bend and shape it so it converges into a single point of focus, known as the “optical center.” It is important to note that this measurement is determined with the camera focused on infinity and that lenses are named by their focal length which can be found on the barrel of the lens.
How to Use Focal Length
Now that you know what focal length is and its effect on photography, how do you use it?
Short focal length
Short focal length lenses are used in architectural, documentary, and landscape photography because they have a wide angle of view. These wide-angle lenses make subjects appear smaller, which requires photographers to stand closer to fill the frame. Short focal lengths are suitable for environmental portraiture, large groups, and small spaces.
Keep in mind that photos taken at short focal lengths will often experience distortion, particularly around the edges. It’s important to take care if you want to maintain straight lines.
Standard focal length
50mm is generally considered the focal length that most closely approximates the human field of view. Focal lengths closer to 50mm are flexible and used for almost every genre of photography, aside from niche genres that require specialized lenses.
Long focal lengths
Focal lengths from 70mm to 85mm and above are generally considered longer focal lengths, and they’re often referred to as “telephoto lenses.” Whether you use zoom lenses or prime lenses, you can expect to see compression of distance and less distortion in longer focal lengths.
This allows photographers to keep distance between themselves and their subjects. As a result, these focal lengths are ideal for situations where you may want to remain unobtrusive, such as sports, wildlife, or wedding photography.
Sensor size
While the lens controls the angle of view, the field of view in a photograph depends on interaction between the focal length and the camera sensor. Full frame camera sensors capture the full angle of view that the focal length can deliver, but crop sensors can’t capture all the data adequately. So, depending on the crop factor of the sensor, a 35mm focal length could look more like 50mm.
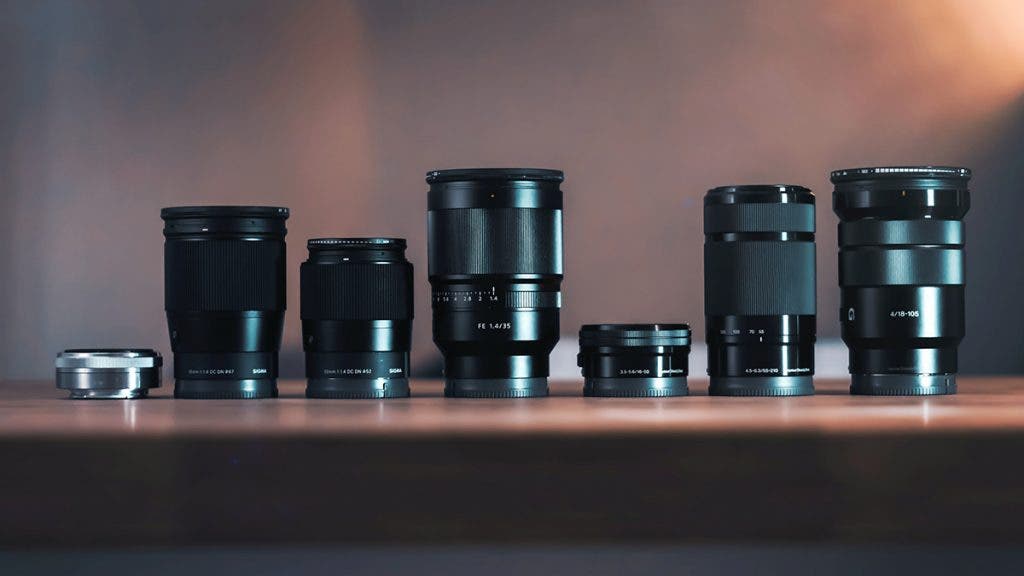

Focal Length Comparison in Lenses
Lenses have a large range of focal lengths from extremely short like 8mm, to extremely long like 600mm and beyond. The best focal length for a photograph varies based on the subject matter and situation. Fortunately, with a DSLR, mirrorless, or other interchangeable lens camera, you can choose the right focal length every time you shoot.
Wide angle lens
Example lenses: Full-frame approx. 14 – 35mm / Crop sensor approx. 10 – 24mm
Short focal length
Short focal length lenses are used in architectural, documentary, and landscape photography because they have a wide angle of view. These wide-angle lenses make subjects appear smaller, which requires photographers to stand closer to fill the frame. Short focal lengths are suitable for environmental portraiture, large groups, and small spaces.
Keep in mind that photos taken at short focal lengths will often experience distortion, particularly around the edges. It’s important to take care if you want to maintain straight lines.
Standard lens
Example Lenses: Full-frame approx. 50 – 60mm / Crop sensor approx. 35mm
50mm (or the nifty fifty) is generally considered the focal length that most closely approximates the human field of view. Focal lengths closer to 50mm are flexible and used for almost every genre of photography, aside from niche genres that require specialized lenses.
Telephoto and Super Telephoto Lenses
Example Lenses: Full-format approx. 70 – 200mm / Crop sensor approx. 55 – 200mm; Full-frame approx. 300 – 600mm / Crop sensor approx. 200 – 600mm
Focal lengths from 70mm to 85mm and above are generally considered longer focal lengths, and they’re often referred to as “telephoto lenses.” Whether you use zoom lenses or prime lenses, you can expect to see compression of distance and less distortion in longer focal lengths.
This allows photographers to keep distance between themselves and their subjects. As a result, these focal lengths are ideal for situations where you may want to remain unobtrusive, such as sports, wildlife, or wedding photography.
Macro Lens
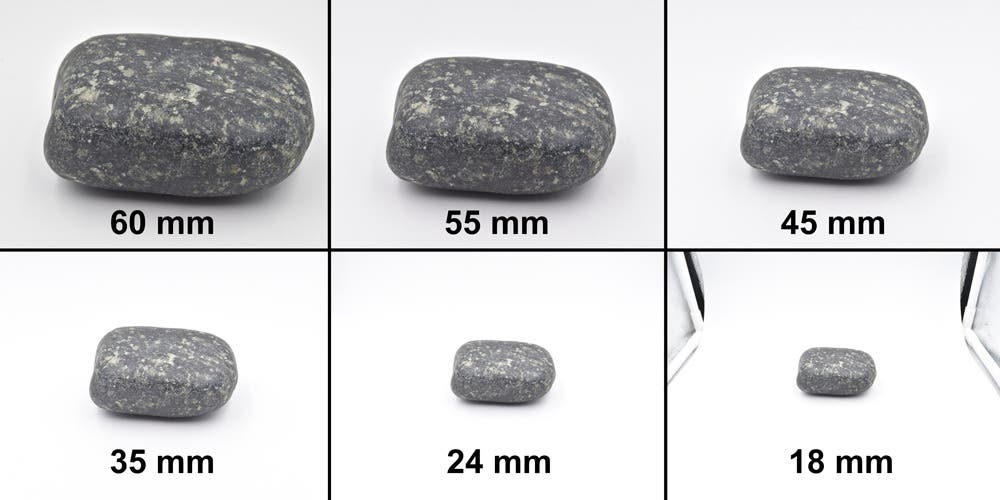
A macro lens, used for close-up photography of small subjects like flowers and insects, lets the photographer get physically close to the subject and show it as larger than life within the frame. Macro lenses can have a focal length ranging from 60mm to 200mm. The best focal length is the one that lets you maintain an appropriate distance from the subject.
You can photograph unmoving objects like rocks, shells, and plants more easily with a shorter focal length, while moving subjects or living creatures are easier to capture with longer focal lengths.
Why is focal length important?
It’s important for photographers to know the practical effects that focal length has on image-making. The focal length of the lens impacts three key areas:
Angle of view
How much of the scene a lens shows to the camera sensor. Shorter lens focal lengths have wide angles of view, while long focal lengths have narrower angles of view. Mid-length, around 50mm, have a similar angle of view to the human eye.
Subject size
The distance between the photographer and the subject, objects will appear smaller in images taken with short focal length lenses, and larger in those with longer focal lengths.
Compression
Is the distance between subjects in a scene. Longer focal lengths compress the distance, making it appear as if the foreground, middle, and background are closer together.Shorter focal lengths increase the appearance of distance between planes.

Lens Focal Length vs Camera Focal Length
Because cameras feature a variety of sensor sizes, not all models will tell you the true focal length of a lens. Lens focal length is based on a 35mm sensor size, based on 35mm film. Most full frame camera sensors are the equivalent of 35mm, so a 100mm lens will actually have a 100mm focal length.
In a crop sensor camera, the sensor is smaller and will magnify the image accordingly. Canon’s crop sensor will effectively magnify the image by 1.6x. That means a photograph taken with a 100mm lens will be the equivalent of a 160mm (or 1.6 times the focal length).
Nikon’s crop sensor cameras have a 1.5x magnification, so that same 100mm lens will be the equivalent of 150mm. Some cameras have even smaller sensors, so the magnification will be larger. It’s important to know if your camera has a magnification factor so you can predict focal length adjustments accordingly.
Zoom vs Prime Lens
Some lenses have a variable focal length (like 18-55mm or 70-200mm) and are called zoom lenses, while others have a fixed focal length (like 50mm or 100mm) and are referred to as prime lenses. The choice between a zoom lens and prime lens is often based on preference and subject matter.
For travel photography, using a zoom lens is convenient because you can achieve a variety of focal lengths with the same lens, allowing you to you carry less equipment. Some photographers prefer prime lenses because they often feature higher quality glass and wider apertures. Ultimately, the decision comes down to personal preference.

Suggested focal length based on type of photography
Portraits
For portrait photography, you want to choose a focal length that will be flattering to the subject. Try to avoid wide angle lenses, especially if the person is close to the camera or positioned off center as this can exaggerate features. For a head and upper body composition, 50mm is great. If getting a tighter view of the head and shoulders, try 85-90mm. For a pure headshot, then 135-200mm is recommended.
Street
For street photography, 35mm and 50mm are the most popular. The 50mm allows for a more intimate composition, while 35mm will include more of the surrounding to establish context. Some have also recommended 28 or 24mm to provide an even larger field of view to give a better sense of the environment. Often with such wide focal lengths, you’ll want to be closer to the subject.
Architecture
Classic architecture images of interiors and large building are often taken with an ultrawide angle lens, usually in the 14-21mm range. The wide angle allows you to capture more of the subject in tight environments. The demagnification can also make an area appear more spacious. It’s important to keep the lens/camera system level so straight lines are not distorted.
Landscape
Great landscapes can be made with any focal length, depending on the composition and feel you’re after. “Classic” landscapes with well-defined foreground, midground, and background elements are usually shot with an ultrawide or wide-angle lens (16-24mm range). For the “compressed” look where far away objects appear close to each other, a telephoto range (200-400mm) may be used.
Wildlife and Sports
Most will agree that wildlife and sports are best shot with a long telephoto lens, typically greater than 400mm, depending on the animal and event. In fact, one of the golden rules in bird photography is, “No matter how long your lens is, it’s never long enough.”
Conclusion
Once you understand the practical nature of how focal length functions in photography, you’ll be better prepared to choose the proper focal length for your next shoot. Are you looking for a new lens for your camera? Or maybe you want to revamp your setup entirely with a new camera? At Adorama, we have everything you need to get started, with great products from Nikon, Canon, Sony, Fujifilm, Olympus, Panasonic, and other fantastic brands.






